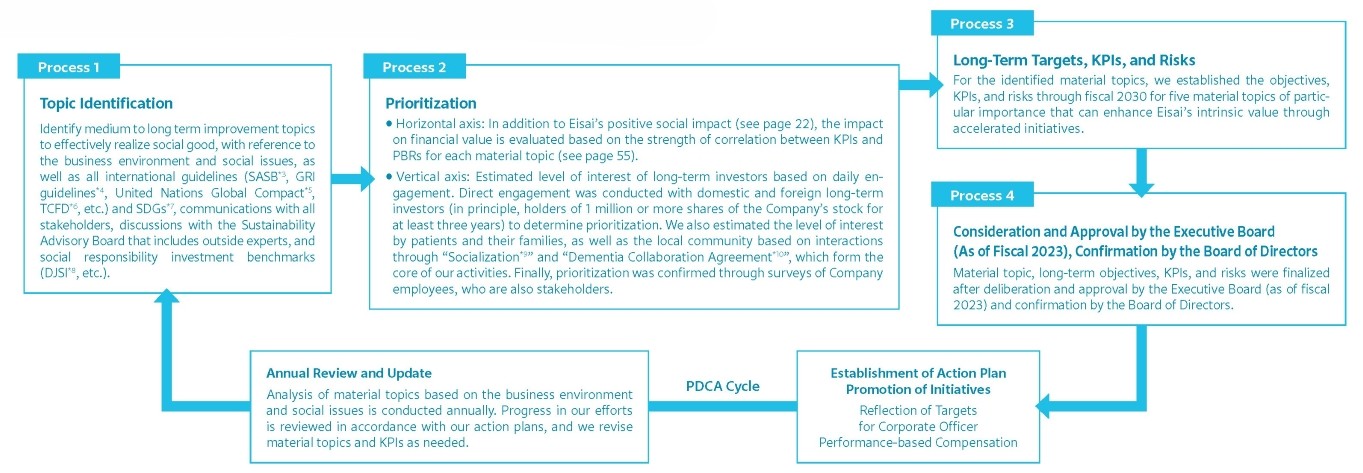
Identifying Our Materiality
At Eisai, in order to clearly identify priority issues to be addressed to maximize corporate value over the medium to long term through the realization of our corporate concept, we are identifying materiality to effectively realize social good in accordance with our Articles of Incorporation, amended in June of 2022.
The horizontal axis for materiality is “Eisai’s Intrinsic Corporate Value (social impact + financial value)”, as we understand the importance of creating social impact and creating financial value by working toward the effective realization of social good.
The vertical axis is “Stakeholders’ Interests”. Based on the concept that it is efficient to focus on long-term investors, who are the beneficiaries of residual income, in order to sustainably maximize corporate value in a way that satisfies all stakeholders*1, we have adopted a method of identifying and prioritizing the interests of long-term investors. At the same time, for this materiality, we have set the vertical axis so that it can be correctly understood that it is intended to create long-term benefits not only for long-term investors, but also for a wide range of stakeholders.
In accordance with the above two axes, we have identified 15 material topics. Among them, we have identified five topics of great interest to our stakeholders, especially long-term investors, that have a positive social impact and correlation with PBR, which we believe will enhance our intrinsic corporate value through our accelerated efforts, and we have established long-term objectives, KPIs, and risks for fiscal 2030. The new materialities and long-term goals, KPIs, and risks were set after deliberation and approval by the Executive Board (as of fiscal 2023*2) and with confirmation by the Board of Directors. Every year, we conduct reviews on the progress of these activities and aim to ensure their promotion through the PDCA cycle.
Furthermore, every year we conduct an analysis of our material topics in light of the business environment and social issues. We review progress in our efforts in accordance with our action plans, and revise our material topics and KPIs as needed.
-
*2 Changed name to Growth & Operating Committee (GOC)
Process of Identifying New Material Topics to Effectively Realize Social Good
*3 Sustainability disclosure standards provided by the IFRS that identify material topics by industry
*4 Indicators that concretely visualize the abstract concept of sustainability by the NPO Global Reporting Initiative, whose mission is to set international standards for sustainability
*5 Global framework launched in 2000 to realize sustainable growth
*6 Private sector-initiated Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
*7 International indicators chosen by the United Nations in September 2015, and set forth in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
*8 ESG indexes of U.S. company S&P Global to evaluate the sustainability of companies
*9 Toward realizing our corporate concept, spending time with patients and the people in the daily living domain or sharing experiences with them such as eating or working together in order to learn how they feel
*10 An initiative to conclude collaborative agreements with local governments and groups to create projects to identify and relieve the anxieties of local residents regarding people affected by dementia
Materiality Toward Effective Realization of Social Good through the hhc Ecosystem
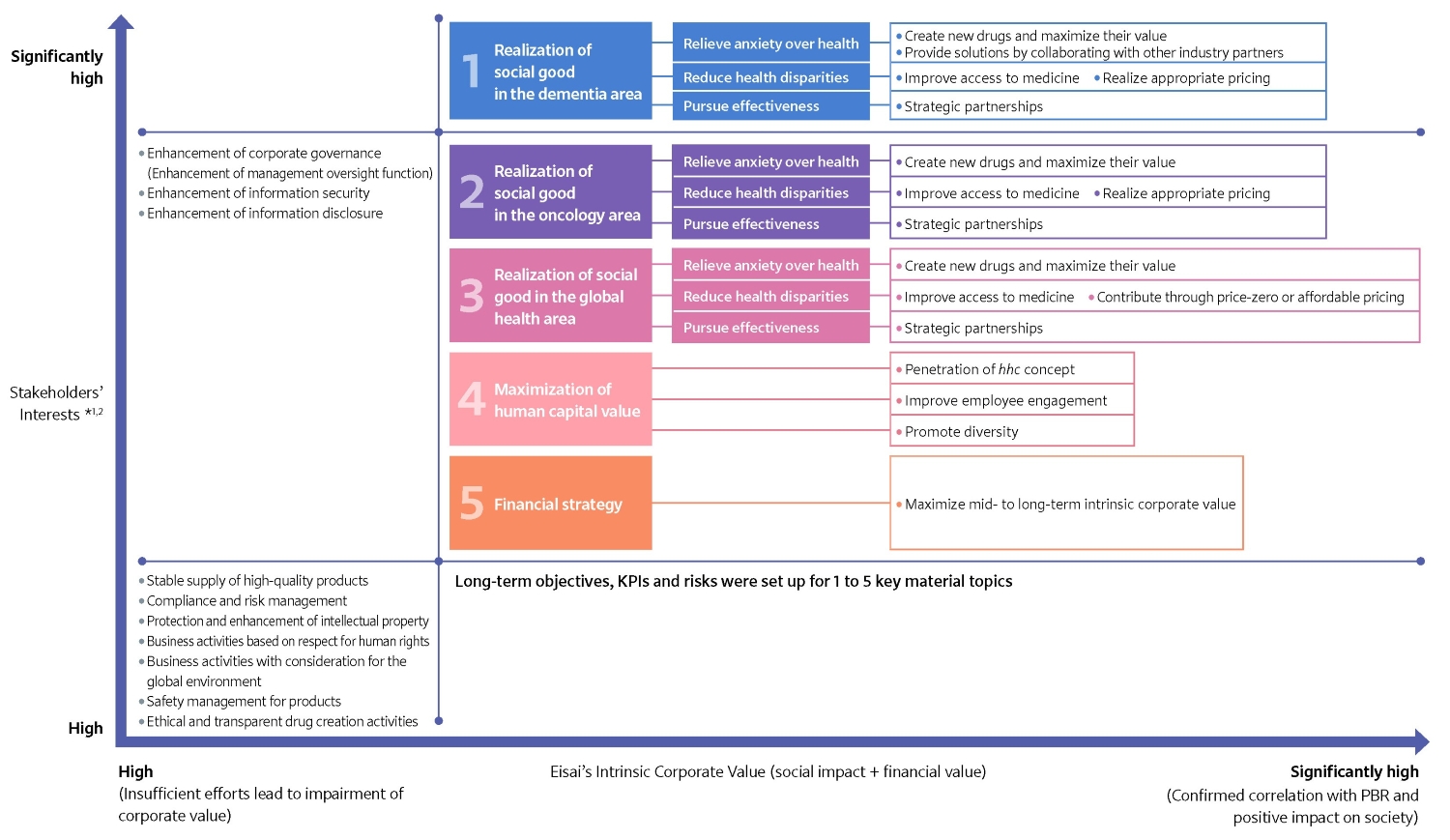
*1 Stakeholders: Long-term investors (shareholders), patients and their families, employees, and the community
*2 For the material topics other than 1 to 5, the importance of the material topics within the same quadrant are equal
Related pages
- Realization of social good in dementia area
- Realization of social good in oncology area
- Realization of social good in global health
- Maximization of the value of human resources
- Financial strategies
- Enhancement of corporate governance (Enhancement of management oversight function)
- Enhancement of information disclosure
- Enhancement of information security
- Stable supply of high-quality products
- Compliance and risk management
- Protection and enhancement of intellectual property
- Business activities based on respect for human rights
- Environmentally friendly business activities
- Safety management on products
- Ethical and transparent drug discovery activities
1. Realization of Social Good in the Dementia Area
Long-term objectives, KPIs, and risks
*You can scroll to the left or right here
| FY2024 Progress |
Early establishment and maximization of value for the LEQEMBI®*1 business |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| FY2025 targets and KPIs |
Early establishment of LEQEMBI® business and its value maximization
• Early realization of approval and launch in all five regions*5
• Contribute to approx. 35,000 people living with AD a year globally and generate social impact of approx. 80 billion yen in the U.S.*6
• Approved for intravenous infusion maintenance and subcutaneous formulations
• Collaborate with partners to quickly realize the use and dissemination of blood-based biomarkers as the definitive diagnostic tool for AD
|
||
| FY2030 targets and KPIs |
Realization of a society where people can live with peace of mind when they are diagnosed with AD
• Expand access to LEQEMBI® to contribute to approx. 900,000 people living with AD a year globally. Generate social impact of approx. 1.8 trillion yen in the U.S.
• Develop next-generation dementia treatments following LEQEMBI®, initiate late-stage clinical trials, and submit for multiple projects including the anti-MTBR tau antibody E2814*7
• Provide new solutions that contribute to health and prevention of disease, supporting the daily lives of approx. 10 million people a year globally affected by the disease in collaboration with other industries
|
||
| Goal |
Establishment of a dementia ecosystem that supports and encompasses the people’s entire life from healthy to high-risk state, onset/treatment of disease, follow-up/prognosis by playing the role of a producer |
||
| Major risks |
• Risk that LEQEMBI®’s market penetration would not be achieved as expected due to limitation of healthcare system infrastructure and increased competition in the market |
||
*1 Antibody for Alzheimer’s disease produced as the result of a strategic research alliance between Eisai and BioArctic. Collaboration with Biogen. Generic name: lecanemab
*2 North America
*3 Europe, Middle East, Africa, Russia, Oceania
*4 East Asia Global South, South Korea, Taiwan, India, ASEAN, Central and South America, South Africa.
*5 The "early realization of insurance reimbursement" in all 5 regions, disclosed in Value Creation Report 2023, was revised in Value Creation Report 2024 in light of insurance reimbursement plans in each region
*6 Revised in view of LEQEMBI®’s contribution in fiscal 2024
*7 Investigational. Discovered as part of research collaboration between Eisai and University College London
2. Realization of Social Good in the Oncology Area
Long-term objectives, KPIs, and risks
*You can scroll to the left or right here
| FY2024 Progress |
Value maximization of Lenvima® |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| FY2025 targets and KPIs |
Value maximization of Lenvima® |
||
| FY2030 targets and KPIs |
Contribution to patients with refractory cancers through new projects subsequent to Lenvima® |
||
| Goal |
Cure of refractory cancers by creating innovative treatments, expansion of access, and realization of prevention based on a predictive model of cancer onset |
||
| Major risks |
• Risk of not achieving the expected profits due to discontinuation or delay of the development of new indications for Lenvima® or the development plan of new projects |
||
*1 KEYTRUDA® is a registered trademark of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. Projects for Lenvima® are under joint development with Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA
*2 Due to primary endpoint of clinical study for non-small cell lung cancer, etc., not being achieved, the "product sales at the 500 billion yen level" disclosed in Value Creation Report 2023 was revised in Value Creation Report 2024
*3 Regarding BB-1701, because it was agreed that future global expansion and promotion will be implemented by Bliss Biopharmaceutical Co. Ltd., on its own, and Eisai decided not to exercise the option for a strategic partnership agreement, this has been removed
3. Realizing Social Good in the Global Health Area
Long-term objectives, KPIs, and risks
*You can scroll to the left or right here
| Progress until FY2024 |
Lymphatic filariasis (LF) Malaria |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| FY2025 targets and KPIs |
LF Mycetoma Malaria |
||
| FY2030 targets and KPIs |
LF Mycetoma Malaria |
||
| Goal |
Contribute to the eradication of diseases and reduction of health disparities through the creation of new treatments and expanded access |
||
| Major risks |
• Risk of delays in elimination activities due to the deprioritization of LF countermeasures in endemic countries |
||
*1 Based on the WHO LF elimination target by 2030
*2 Revised the fiscal 2025 target based on the latest WHO updates reflecting the suspension and delays of MDA due to the deterioration of political conditions and the spread of COVID-19 in LF-endemic regions
*3 In Value Creation Report 2024, we showed the social impact from MDA implementation as impact from DEC tablets proportionally distributed under the assumption of administration of two drugs, in light of the addition of new treatments (three-drug administration) to the WHO treatment guidelines, the combined drugs in achieving LF elimination, and the importance of the various partnerships, we have made the change to show the whole social impact from MDA implementation, and not just the social impact from DEC tablets
*4 Plan to revise KPI in response to expected changes to the LF elimination roadmap to 2030 by the WHO in 2025
For details, please visit here.
4. Maximization of Value of Human Resources
Long-term objectives, KPIs, and risks
*You can scroll to the left or right here
| Fiscal 2024 Progress |
Penetration of the corporate concept hhc Increased employee engagement Enhancement of women’s participation to incorporate diversity Employee Impact |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| FY2025 targets and KPIs |
Penetration of the corporate concept hhc Increased employee engagement Enhancement of women’s participation to incorporate diversity Employee Impact |
||
| FY2030 targets and KPIs |
Penetration of the corporate concept hhc Increased employee engagement Enhancement of women’s participation to incorporate diversity Employee Impact |
||
| Goal |
Enhancement of corporate value through solutions and innovation brought that maximize the strengths and characteristics of diverse human capitals |
||
| Major risks |
• Risk of difficulty in succession for important global positions |
||
5. Financial Strategies
Long-term objectives, KPIs, and risks
*You can scroll to the left or right here
| Fiscal 2024 Progress |
Optimal capital structure and financial soundness Achieve both stable dividends and investment for growth |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| FY2025 targets and KPIs |
Expansion of intrinsic corporate value (social impact + financial value) by expansion of contribution through LEQEMBI® and DEC tablets Pursue an optimal capital structure while ensuring financial soundness Achieve both stable dividends and investment for growth |
||
| FY2030 targets and KPIs |
Maximization of intrinsic corporate value while the company is in rapid growth Increase financial robustness and secure growth investment capacity |
||
| Goal |
Maximize mid- to long-term intrinsic corporate value
|
||
| Major risks |
• Risk of not earning the expected revenue from LEQEMBI® and Lenvima® |
||
*1 Rating by Rating and Investment Information, Inc. (R&I) (as of May 30, 2025)
*2 An indicator to evaluate whether the company is efficiently generating social impact; the sum of the social impact of LEQEMBI® and DEC tablets was divided by equity. Calculation was based on those two important products in which the estimation of social impact was completed
