Policy and Basic Concept
As a global healthcare company, the Eisai Group has established the ENW (Eisai Network Companies) Environmental Protection Policy and conducts business activities with an emphasis on global environmental protection. The policy states: “Contribute to the formation of a recycling-oriented society by promoting the sustainable use of resources, including water, along with waste reduction and recycling”. In line with this policy, we promote proper waste management and resource recycling initiatives globally to reduce waste generation, improve recycling rates, minimize final landfill volume, and reduce hazardous waste, on a global scale.
Targets and Actions
-
The Eisai Group has established mid-term goals on a global basis.
-Total waste; Reduction of the amount ratio of total waste / net sales by 7% from FY2023 levels
-Landfill disposal; Waste landfilled / Waste generated ratio < 2%
-Recycling ratio (including valuable sales); 50% or more (including thermal, chemical, and material recycles)
-Hazardous waste; Reduction of the amount ratio of hazardous waste / (net sales plus R&D expenses) by 7% from FY2023 levels
In addition, the Eisai Group in Japan has set the following targets.
-Zero emissions; Waste landfilled / Waste generated ratio < 0.5%
-Waste plastic recycling ratio (including valuable sales); 80% or more
Structures and Systems
The Eisai Group has established an environmental management system to promote global activities and is working to strengthen activities to identify environmental risks and establish countermeasures in Japan and overseas.
Promotion Structure and Environmental Audit
https://www.eisai.com/sustainability/environment/management/structure/index.html
Initiatives
We implement thorough waste segregation at our sites, selection of waste management contractors that actively promote resource recycling, and work to recycle and sell recovered organic solvents used in the chemical synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (auxiliary fuel for waste solvents).
We also promote the recycling of waste plastics as raw materials for RPF (solid fuel), thermal recycling, and recycling of PTP (press through pack) sheet scraps generated in the packaging process.
In April 2022, the “Act on Promotion of Resource Circulation for Plastics” was enforced in Japan, in response to the recent increase in the importance of controlling the use of plastic resources and resource recycling. The Eisai Group in Japan are promoting efforts to reduce the volume of waste plastic generated to less than 250 tons.
In addition, we are promoting the use of paper waste by minimizing the use of office automation paper, digitizing stored documents, and promoting the sale of used paper as valuable resources.
Furthermore, we are encouraging our suppliers to set goals and promote initiatives for “Recycling of resources” through briefings and engagement activities.
-
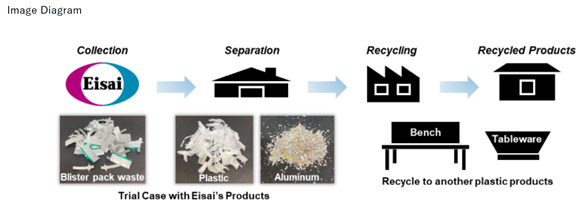
- <Recycling of PTP Sheet Scraps>
-
PTP sheets, mainly made from plastic and aluminum, are used for packaging of medicines. The manufacturing processes of the sheets generate plastic waste, including the sheet scraps. Eisai’s Kawashima Plant (Gifu Prefecture), has so far mainly employed thermal recycling (a method to collect and use thermal energy from waste incineration) systems to dispose of plastic waste.
Since April 2024, Eisai Co., Ltd. has been aregistered as a Kakamigahara SDGs Partners, supporting initiatives of Kakamigahara City, where the Kawashima Plant is located. In collaboration with Matsuda Sangyo Co., Ltd. (headquartered in Tokyo), which operates a plant in Seki City, Gifu Prefecture, we successfully established a scheme to separate PTP sheet scraps into plastic and aluminum, enabling material recycling of each component. This initiative has led to a reduction in CO₂ emissions associated with incineration. We are currently exploring ways to commercialize and utilize the recycled plastic.
PTP Sheet
Data
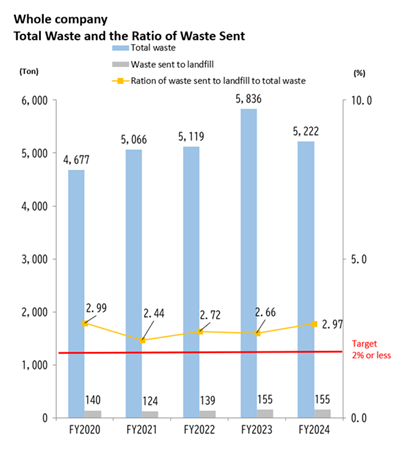
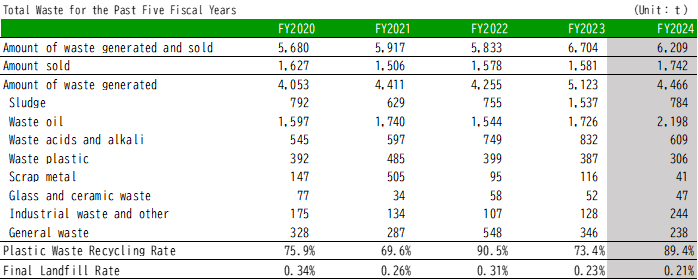
Progress toward the 2030 waste reduction target was evident in FY2024 results, with an indicator value of 0.661 (tons of waste per 100 million yen in sales revenue), below the FY2024 target of 0.773. Total waste generation was 5,222 tons, a decrease of 614 tons from the previous year. This improvement was primarily due to the absence of inventory disposal activities that occurred in FY2023, following the end of the COVID-19 related disruptions. During that period, large volumes of antibacterial sprays and wet wipes were discarded, resulting in increased mixed sludge generation.
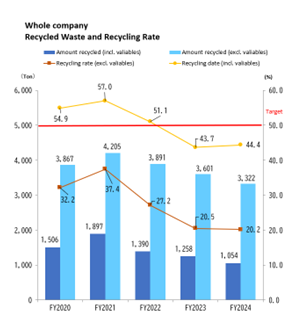
The total volume of recycled waste, including valuable materials, was 3,322 tons, a reduction of 279 tons compared to the previous year. This outcome was due to a change in waste disposal contractors. Although efforts were made to promote domestic recycling of PTP sheet scraps and other materials, the contractor that had enabled full recycling in FY2023 ceased operations, necessitating a transition to a new service provider. On the other hand, the recycling rate (including valuable materials) rose to 44.4%, up 0.7 percentage points from the previous fiscal year. Although the total amount of recycled materials (including valuable materials) decreased from the previous year, the amount of waste generated also declined, resulting in an overall increase in the recycling rate.
As a result, the final landfill volume remained unchanged at 155 tons, while the final landfill rate increased to 2.97%, up 0.31 percentage points from the previous year. Although the landfill volume was consistent year-on-year, the overall reduction in waste generation led to a proportionally higher landfill rate.
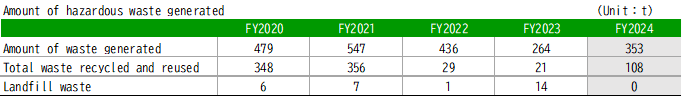
Progress toward the Medium-Term Target for Hazardous Waste Reduction was reflected in the FY2024 results, with an indicator value of 0.119 (tons of hazardous waste per combined total of R&D expenses and cost of sales in 100 million yen), exceeding the FY2024 target of 0.107. Total hazardous waste generation reached 353 tons, an increase of 89 tons compared to the previous year. This increase was primarily due to the discovery of contaminated soil that failed to meet regulatory standards at the site adjacent to the new injectable drug and research building at the Kawashima Plant in Gifu Prefecture. The entire volume of contaminated soil was excavated and removed.
In Japan, the landfill ratio was 0.21%, achieving zero emissions (Waste landfilled/Waste generated ratio<0.5%) for the 17th consecutive year. The waste plastic recycling ratio (including valuable sales) was 89.4%, achieving the target of 80% or more.
<Waste Generation>

<Hazardous Waste Generation >

Onsite Inspections of Processing-Waste Companies
The Eisai Group in Japan outsources the collection, transportation, intermediate treatment, and final disposal of waste mainly to top-quality industrial waste disposal companies and periodically conducts onsite inspections of contractors. In FY2024, the Eisai Group in Japan conducted a total of 31 on-site inspections including remote inspections.