
Clinical development is an important research process for verifying the safety and efficacy of new drugs. This process confirms that the drugs are indeed effective and safe for patients. Clinical development is usually divided into the following stages.
Phase I Trial : The safety of the drug is confirmed in a small number of healthy volunteers
Phase II Trial : The efficacy and safety of the drug are confirmed in a small number of patients
Phase III Trial : The efficacy and safety of the drug are confirmed in a large number of patients, and final data is collected
Phase IV Trial : Even after the drug is on the market, insights into its long-term efficacy and safety are obtained
In recent years, there is increased attention on designing clinical studies utilizing medical data known as real-world data. Real-world data includes anonymized treatment histories, prescription histories, and clinical test data from patients at medical institutions. Analyzing these data allows researchers to identify what treatments patients are currently on and provides hints as to which treatments can alleviate patients’ concerns.
Example of Real-World Data Analysis
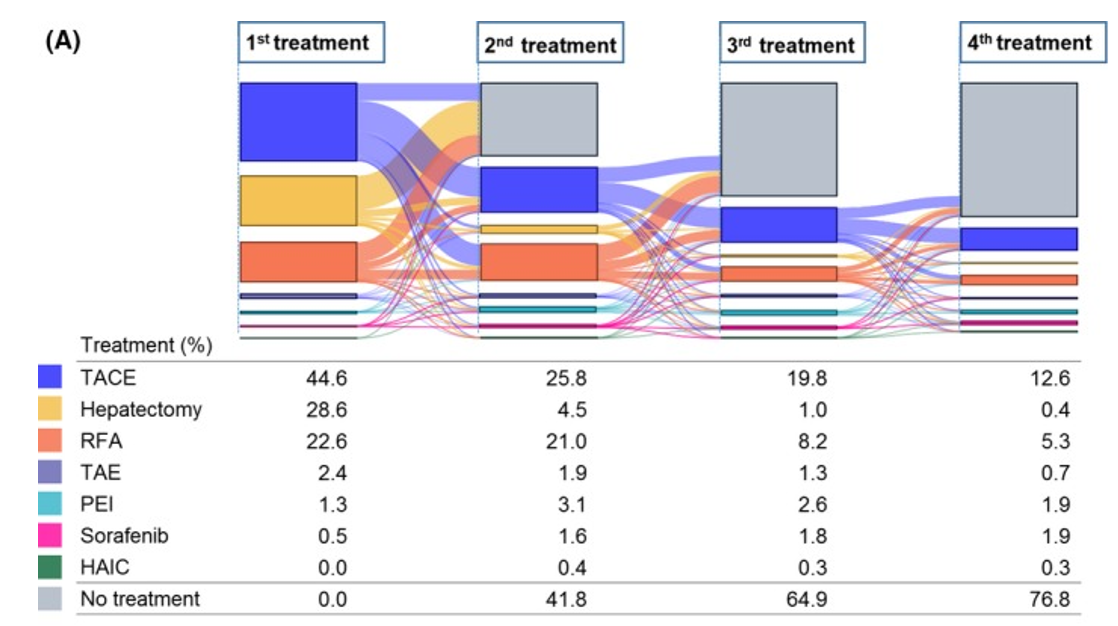
References
-
1) Akada et al. Database analysis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and treatment flow in early and advanced stages. Pharmacol Res Perspectives. (2019)
